

However, since males have only one X chromosome and one Y chromosome, they do not have a spare IL2RG gene.
Thus, it is a critical component for mobilizing the body's defenses against infection.īecause females have two X chromosomes, if they have a mutation that disrupts the IL2RG gene on one X chromosome, they still have a spare normal gene on the other X chromosome that can compensate for the mutation.
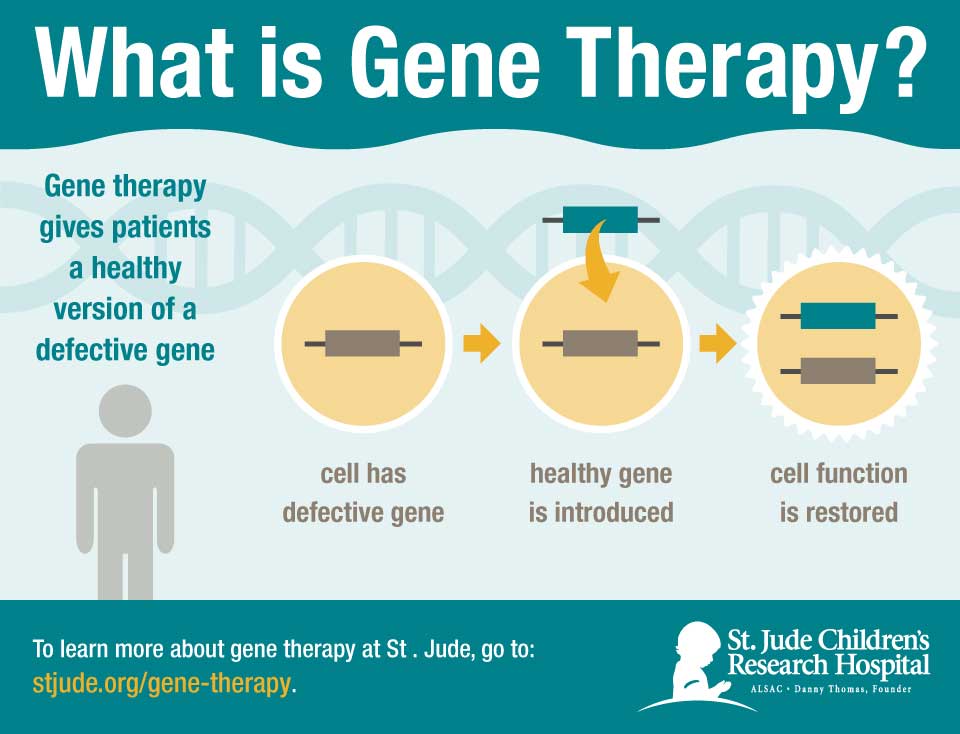
The defective part of the lymphocyte receptor is called the "common" gamma chain, because it is a common component of lymphocyte receptors for several types of cytokines, including the interleukin-2 (IL-2) receptor. This gene creates a key part of a receptor on the surface of a lymphocyte which, when activated by chemical messengers called cytokines, transmits information that directs lymphocytes to mature, proliferate and mobilize to fight infection. X-linked severe combined immunodeficiency (XSCID) is caused by mutations in a gene on the X chromosome called IL2RG. Children with untreated SCID rarely live past the age of two. Because children with SCID experience multiple infections, they fail to grow and gain weight as expected (i.e., failure to thrive). The classic symptoms of SCID include an increased susceptibility to a variety of infections, including ear infections (acute otitis media), pneumonia or bronchitis, oral thrush (a type of yeast that multiplies rapidly, creating white, sore areas in the mouth), and diarrhea. Another form of SCID is caused by a deficiency of the enzyme adenosine deaminase (ADA), normally produced by a gene on chromosome 20. Severe combined immunodeficiency, or SCID, is a term applied to a group of inherited disorders characterized by defects in both T and B cell responses, hence the term "combined." The most common type of SCID is called XSCID because the mutated gene, which normally produces a receptor for activation signals on immune cells, is located on the X chromosome. The antibodies attack foreign substances, or antigens, that mark invading viruses, bacteria and fungi. Normally, T cells encourage other immune cells to respond to foreign substances as well as directly combat certain viral and fungal infections. Each specialized type of cell is responsible for a particular immune response. Others remain in the bone marrow where they mature into B cells and natural killer cells. Some lymphocyte precursors move to the thymus gland, where they become T cells. Lymphocytes, a type of white blood cell, are made from blood forming precursors, or "stem," cells in the bone marrow. These pioneering patients are still alive and continue to participate in on-going studies by physicians at the National Human Genome Research Institute. In addition, one form of SCID became the first human illness treated by human gene therapy in 1990, a process in which a normal gene was transferred into the defective white blood cells of two young girls to compensate for the genetic mutation.
#GENE THERAPY SCID FREE#
David died in 1984 following an unsuccessful bone marrow transplant, an attempt to provide him with the capacity to fight infections on his own and thus free him from the bubble.Īlthough a rare disease, SCID has been extensively studied over the past several decades because of the insights it provides into the workings of the normal human immune system. He lived in such isolators for nearly 13 years.

Because David's brother had died of the disease, doctors immediately placed him into a plastic isolation unit to protect him from infections. Caused by defects in any of several possible genes, SCID makes those affected highly susceptible to life-threatening infections by viruses, bacteria and fungi.
#GENE THERAPY SCID MOVIE#
Severe Combined Immunodeficiency (SCID) may be best known from news stories and a movie in the 1980s about David, the Boy in the Bubble, who was born without a working immune system.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
